From Passive Relief to Predictive Performance
In a world where burnout is the baseline and biofeedback is king, recovery is no longer optional—it’s strategic.
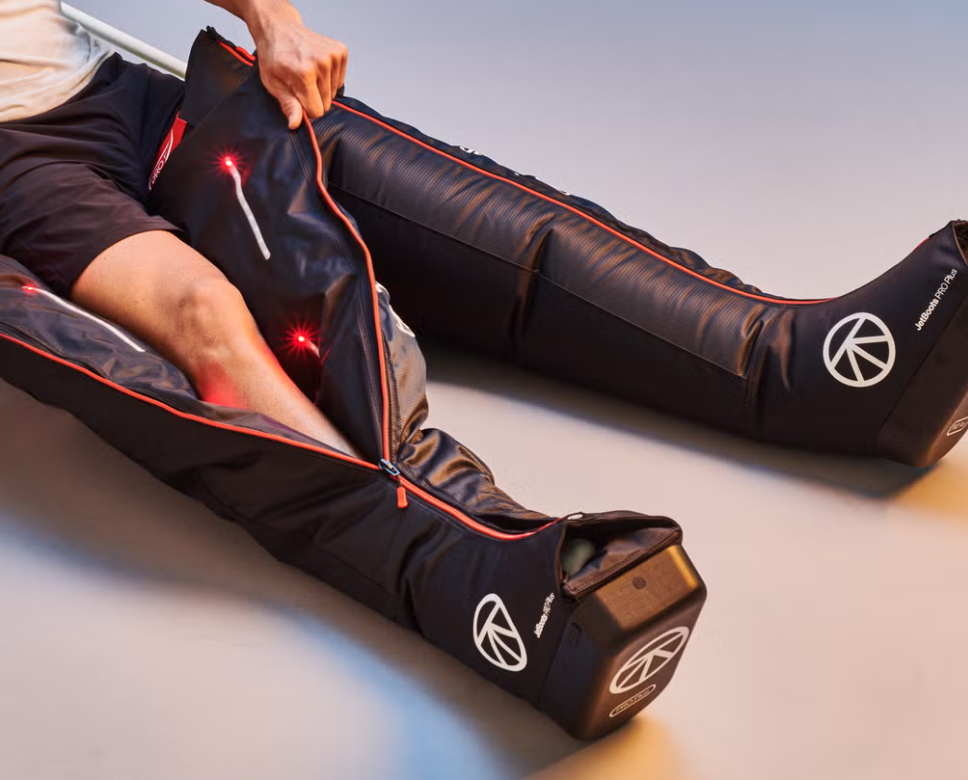
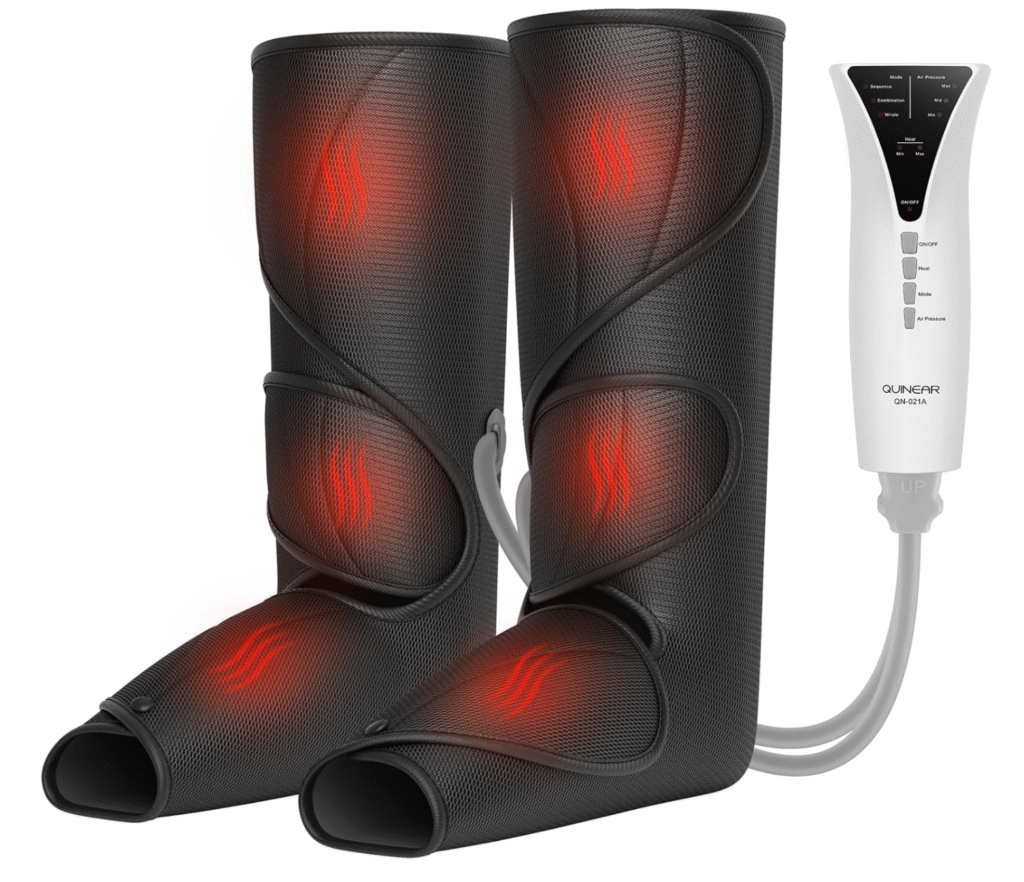
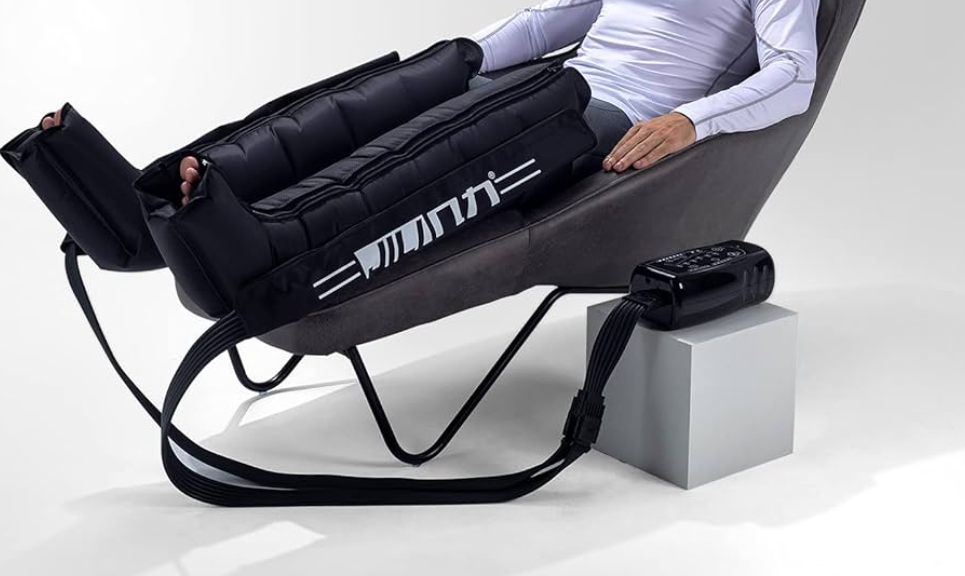
The NormaTec Pulse 2.0 isn’t just a recovery device.
It’s a physiological upgrade.
A wearable wellness system.
A performance tool trusted by elite athletes, physical therapists, and tech-savvy optimizers alike.
And if you’re not already using smart compression therapy, your recovery routine is stuck in 2012.
The Feeling: Like Wrapping Your Legs in a NASA-Controlled Hug
This isn’t your average massage.
This is an intelligent system that senses, adjusts, and restores like it’s reading your mind—and your muscles.
The NormaTec Pulse 2.0 uses dynamic air compression that syncs with your body’s rhythm, mimicking the natural muscle pump of your legs.
It boosts circulation, flushes waste, and relieves soreness—all while you sit back and let it do the thinking for you.
👉 And once you experience recovery that thinks for you, you’ll never go back to static foam rollers and guesswork.
Want to see how it stacks up against other top compression boots for circulation? We compared them.
Smarter Recovery: AI + Compression Therapy
We’re living in the era of bio-intelligence.
Your watch tracks your sleep.
Your ring logs your HRV.
But your recovery? Still stuck on “manual mode”?
Not anymore.
NormaTec’s future potential is already taking shape—real-time adaptive pressure based on:
- Heart rate variability (HRV)
- Sleep quality
- Cortisol fluctuations
- Gait asymmetry & fatigue signals
Think of it as a physiotherapist, AI assistant, and blood flow optimizer… in your living room.
No more guesswork. No more soreness surprises.
Just predictive, personalized recovery.
Learn how often you should use leg compression machines.
Nervous System Synergy: Neuroadaptive Recovery
Recovery isn’t just physical.
It’s neurological.
Studies show that rhythmic compression can calm the nervous system, lower perceived pain, and even influence brainwave states.
NormaTec isn’t just helping your legs feel better—it’s helping your whole body relax, reset, and perform better.
“External compression has been shown to reduce sympathetic nervous system activity and promote parasympathetic tone, improving both recovery and mental state.”
— Dr. Andrew Huberman, Neuroscientist, Stanford University
Future integrations with vagal tone sensors and brainwave monitors could make each session a form of meditative recovery—one that aligns your physiology with your psychology.
This isn’t just leg care. It’s nervous system alignment.
Suffer from RLS? Here’s the best leg massager for restless legs.
Pros & Cons of the NormaTec Pulse 2.0
Let’s break it down—what’s fact, not fluff.
Pros
- Trusted by pros, recovery clinics, Olympians
- App-controlled zone targeting + pressure levels
- Exceptional for circulation, fatigue, and lymphatic drainage
- Pairs perfectly with wearables for total recovery intelligence
- Portable enough to use from couch to carry-on
“Pneumatic compression systems like NormaTec aren’t just about comfort—they improve venous return, reduce inflammation, and accelerate lymphatic drainage.”
— Dr. Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES
Cons
- Higher price point than casual massagers
- May not fit well for users under 5’2″
- Requires consistent use to unlock full benefits
- Battery pack sold separately
- Doesn’t include biometric sensors (yet)
This isn’t a “nice-to-have.” It’s a need-to-optimize if you’re serious about performance, pain relief, or long-term healthspan.
Frequently Asked: Is It Worth It?
Is NormaTec worth it for non-athletes?
Absolutely. While elite athletes popularized it, NormaTec is a game-changer for anyone dealing with chronic fatigue, leg swelling, circulation issues, or post-surgery recovery.
How long should you use NormaTec each session?
Most users start with 20–30 minutes, 1–2 times a day. For circulation therapy or intense training recovery, up to 60 minutes is common.
What Real Users Are Saying
“This thing replaced my massage therapist. I track HRV daily—now my recovery finally keeps up.”
— Jake M., Ironman Athlete
“I have chronic edema post-surgery. This was the first product that actually gave me relief I could feel in the first session.”
— Linda R., Retired Nurse
“It’s not just a gadget. It’s part of my lifestyle now. My legs are fresher, my sleep is deeper, and I can move again.”
— Darius P., Frequent Business TravelerRehab, Recovery, and Remote Clinical Use
NormaTec isn’t just built for elite athletes.
It’s quietly becoming the gold standard for clinical home recovery, especially in:
- Lymphedema management
- Stroke and vascular rehabilitation
- Senior circulatory support
- Post-operative recovery and inflammation reduction
“Recovery technology is no longer limited to the clinic. With tools like NormaTec, we can prescribe high-grade protocols that patients follow from home—with real results.”
— Dr. Jordan Metzl, Sports Medicine Physician, Hospital for Special SurgeryFrom hospital floors to home care setups, smart compression is no longer a luxury—it’s prescribed performance.
Medical Use FAQ
Can NormaTec help with post-surgery or medical recovery?
Yes—many doctors and physical therapists recommend pneumatic compression therapy to reduce swelling, improve circulation, and speed up healing post-op.Travel, Gravity, and Performance on the Move
From astronauts to esports athletes, the demand for mobile, smart recovery is exploding.
- Jet lag? Combat it with rhythmic lower-body compression.
- Microgravity? NASA has tested similar tech for circulation in space.
- Esports fatigue? NormaTec helps gamers perform longer without swelling or numbness.
Flying soon? Here are compression boots for edema and travel recovery.
Travel Use FAQ
Are compression boots safe for flying or long-haul travel?
Yes. Long periods of sitting increase DVT risk. NormaTec can enhance circulation before and after travel, reducing soreness, swelling, and fatigue.Behavior-Triggered Recovery: When Your Legs Call the Shots
Coming soon: NormaTec that knows you’re fatigued before you do.
Imagine this:
- Your gait shifts subtly → Your app suggests a recovery session
- You undersleep → Your boots recommend light-pressure mode
- You overtrain → Recovery auto-triggers while you Netflix
This is biometric-driven restoration.
It’s proactive.
Preventative.
Personalized.
Want to know what compression really does to your legs? Read our breakdown.
Purchase Decision FAQ
How does NormaTec compare to cheaper leg massagers on Amazon?
Think Tesla vs. golf cart. Cheaper units inflate randomly. NormaTec delivers adaptive, zone-specific pressure backed by sports science and medical data.Compare recovery systems here.
The Road Ahead: Adaptive, Intelligent Recovery
Function Enabled By What It Changes Predictive Recovery Wearables + AI Injury prevention + faster bounceback Neuroadaptive Syncing Brainwave + vagal inputs Deeper relaxation, less stress Clinical Home Use EHR + remote vitals Lymphedema, stroke, senior care Mobile Performance Lightweight form + battery Travel, long-haul flights, esports recovery Biometric Self-Triggering Gait + fatigue signals Proactive sessions before soreness sets in
Final Thought: From Compression to Cognition
This isn’t just about feeling better after leg day.
It’s about redefining what recovery means.
It’s about turning passive relief into adaptive readiness.
NormaTec is no longer a gadget. It’s an extension of your nervous system.
A second skin that listens, adjusts, and helps you show up as your best—even when your body’s not sure it can.
Think about it:
- A device that knows when you’re about to crash
- That responds with tailored, intelligent care
- That fits recovery into your life before your pain forces you to
This isn’t luxury.
It’s the new normal for optimized human performance.
This Isn’t Just a Recovery Tool—It’s a Performance Upgrade You Can Feel
If you’re still using static gear to recover from a dynamic life, you’re already a step behind.
The NormaTec Pulse 2.0 doesn’t just feel amazing—it reads your body, responds to your needs, and helps you bounce back before breakdown hits.
👉 Click here to get the NormaTec Pulse 2.0 now—and feel what elite recovery actually feels like.
Trusted by pro athletes, optimized for everyday recovery, and engineered for people who demand more from their body—this is the tool high-performers don’t just recommend… they refuse to train without it.
You can keep waiting for fatigue to hit… or start training with a system that sees it coming first.